Information
发布时间:2024-01-03

2011年,美国食品药品监督管理局 (FDA) 发布了指导文件《细胞和基因治疗产品效力测试》,主要侧重于效力测试方法。从2011年起,细胞和基因治疗 (CGT) 领域已经取得了重大进展。认识到这一发展,FDA 于 2023 年 12 月发布了题为《细胞和基因治疗产品效力保证》的指导草案。这份新文件超越了单纯关注效力测试,而是采取了更全面的方法来确保整个产品生命周期中的效力。


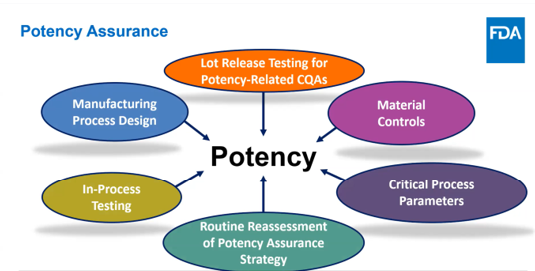

效力放行检测及其放行标准是效力保证策略的重要组成部分
效力保证策略通常应包括多个放行试验,至少包括一个生物分析方法,用于测定产品的相对生物学活性
早期开发阶段 初始 IND 提交 临床开发后期 提交 BLA 之前 效力保证不足可能导致临床暂停

定义产品的 QTPP 并识别与效力相关的 CQA;
What are the key differences between the newly released CGT product efficacy assurance draft by the FDA and the 2011 document(上下滑动查看更多)
·Implement potency tests with appropriate acceptance criteria for in process and lot release testing. 3.Reassess and refine your potency assurance strategy as you increase your understanding of your product and manufacturing process. Potency Assurance and acceptance criteria 1.Potency release assays and their acceptance criteria are essential elements of a potency assurance strategy. ·May include physiochemical assays and bioassays. ·Should have suitable precision, accuracy, specificity, and robustness. ·Minimize assay redundancy. ·Minimize the use of animals in potency assays. ·Should quantitate a potency-related CQA that is at-risk. 2.Potency assurance strategies should typically include multiple release assays, including at least one bioassay that measures a relevant biological activity of the product. Progressive implementations of a potency assurance strategy 1.Your potency assurance strategy may not be fully mature during early development stages, but you should still have a defined potency assurance strategy that includes: ·Identification of initial potency-related CQAs for your product. ·An assessment of risks to potency-related CQAs and measures to mitigate these risks. 2.Include the following information in your initial IND submission: ·Your product’s mechanism of action and QTPP, a list of initial potency-related CQAs and an explanation of how potency-related CQAs were identified. ·A description and justification of your potency assurance strategy. ·General descriptions of your plans for further strengthening your potency assurance strategy during product development (e.g. plan for product characterization and potency assay development. 3.By later stages of clinical development, you should have developed a comprehensive potency assurance strategy: ·Manufacturing process and control strategy should provide phase-appropriate assurance of consistent product potency. ·Control strategy includes at least one assay measuring a potency-related CQA with appropriate acceptance criteria. ·Assays measuring potency-related CQAs are qualified to demonstrate they have adequate performance to confirm that CQAs are within acceptable limits. ·Potency-related CQAs are stable during storage and preparation of the product for administration. 4.Before submitting a BLA, you should use al available product quality and clinical data to reassess and refine your potency assurance strategy. 5.Inadequate potency assurance may lead to a clinical hold: ·For clinical investigations involving significant risk of illness or injury, if the potency of the product is not adequately assured it may be unreasonable to expose subjects to these risks. ·If potency is not adequately assured in a PII or III investigation, the investigation may be considered deficient in design for the following reasons: oReduced statistical power to detect an effect of the product if not all lots have the capacity to achieve the intended therapeutic effect. oinvestigations using lots with unknown or indadequately-controleed potency may not provide sufficient product data to justify spefications of the commercial product. Other topics Recommendations for requesting advice from FDA regarding your potency assurance strategy. General advice for identifying potency-related CQAs and developing a potency assurance strategy throughout the product development lifecycle. Detailed recommendations on the use and development of potency assays and acceptance criteria. Examples of recommended approaches to potency assay selection and design for some CGT product classes. Advice on assay control, qualification/validation, reference materials, and change management. Key points Potency tests are important aspect of potency assurance, but assuring potency requires a broader approach. Develop a potency assurance strategy for your CGT product: ·Define your product’s QTPP and identify potency-related CQAs ·Conduct a risk assessment for each potency-related CQA ·Use a multi-faceted approach to reduce risks to potency-related CQAs, including tests for at-risk potency-related CQAs. ·Take a lifecycle approach to potency assurance-reassess and refine your potency assurance strategy as you gain product knowledge during development.
